
DMARC works alongside SPF and DKIM to prove email sender’s authenticity and adds an additional layer of protection in fighting phishing and email address spoofing.
- DMARC – Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance
- DKIM – DomainKeys Identified Mail
- SPF – Sender Policy Framework
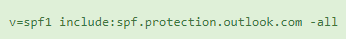
SPF
If you have a fully configured email domain within Microsoft 365, you should already have SPF configured.
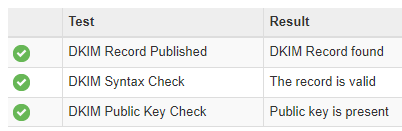
DKIM
To enable DKIM, navigate to Microsoft 365 admin centre > Security > Email & Collaboration > Policies & Rules > Thread Policies > Email authentication settings > DKIM.
Try to enable DKIM for your domain. This will initially fail, but the error message will display the DNS records you need to add for your domain.

Go to your DNS provider admin console and add 2 CNAME records as per the message above. Wait a few minutes and try to enable DKIM again. If it still fails, give it a bit more time.
You can use MX Toolbox to verify that DKIM configuration is working correctly (format: your_domain.com:selector1)
DMARC
The final step is to create another DNS Record for your domain (this time TXT type), i.e.
Name: _dmarc
Value: v=DMARC1; p=quarantine;
This is a very basic example, you can customise it as required:
- p – policy. Instructs the receiving email server what to do with emails that fail DMARC checks. You can set the policy to none, quarantine, or reject.
- pct – the percentage of emails affected by the DMARC. The default value is 100%.
- rua – email address to send aggregate reports of emails failing DMARC. These are sent by the receiving server, normally once a day. No personally identifiable information is included.
- ruf – email address to send forensic reports of emails failing DMARC. These are sent in real time by the receiving server for each failed message. It May contain some identifiable information. Not all email servers will send this type of report.
- fo – failure reporting level. 0 – report is sent when both SPF and DKIM fail. 1 – the report is sent when either SPF or DKIM fails.
- Note: If you are sending DMARC reports to an external domain, the receiving (external) domain must have the following DNS TXT record:
- Name: *._report._dmarc
* wildcard instructs the domain to accept DMARC reports for any other domain. You can replace * with a specific domain. - Value: v=DMARC1
- Name: *._report._dmarc
You can once again use MX Toolbox to verify that DMARC is configured correctly.
Another useful tool is: https://www.learndmarc.com/
November 2024
Oxford, Oxfordshire